Yet another Google ranking factor is about to roll in. And guess what? Like always, web developers and SEO experts are already in pain. Finding it hard to get their head around.
How does this new official ranking factor work? How is it gonna affect website rank? What can one do to maintain or improve their website rank once Core Web Vitals are in place?
So many questions. Essential to be answered for your website.
Just like you, we are also trying to understand the concepts of Web Vitals. So we thought it might be helpful to share what we have learned so far.
In this article, we will walk you through the details of Core Web Vitals. Let’s see if we can find answers together.
A basic concept on Core Web Vitals- The Three Signals
Core Web Vitals are the new Google ranking factor based on user experience.
The search engine giant – Google took this initiative while keeping in mind to serve a great user experience on the internet.
This is surely gonna be the next big element to affect websites’ rank on search results.
The unified guidance intends to ease the process of understanding UX metrics. Now you only have to focus on certain metrics, known as Core Web Vitals.
- Page Loading Speed
- Content Interactivity
- Visual Stability
In the first half of 2020, Google made it public that, Web Vitals is going to be the next official ranking factor.
Since then, three main specifics have been in talks among SEO experts and website owners. Page Loading Speed, Content Interactivity, and Visual Stability.
Technically, LCP, FID, and CLS are those three metrics, collectively named as Core Web Vitals.
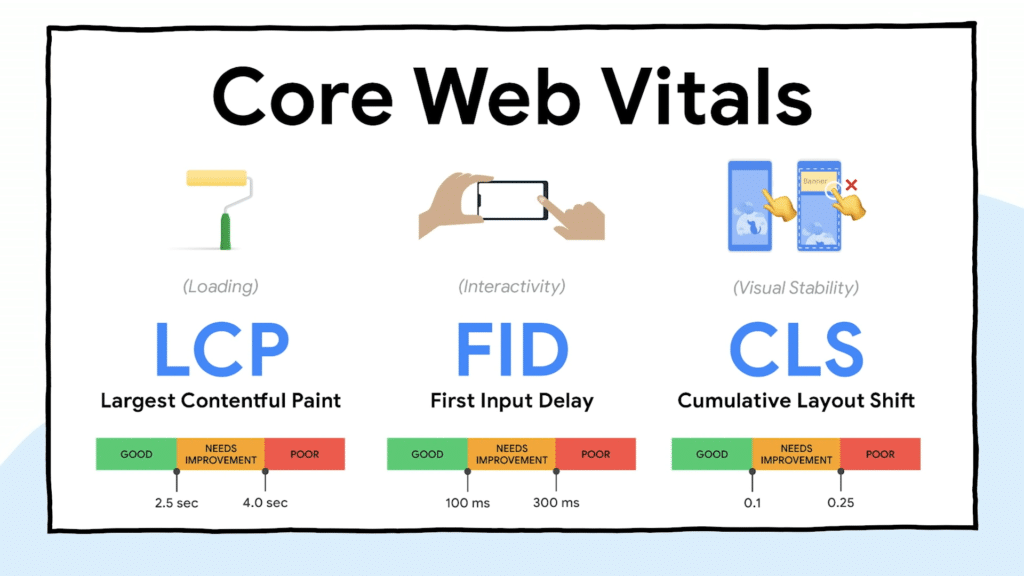
Core Web Vitals.
Photo Source: Google Chrome Developers
Photo Source: Google Chrome Developers
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP)
Your first chance to deliver a good on-page experience is providing a faster loading speed. People don’t like sites that take ages to load.
Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) is the standard that measures sites’ loading performance. This metric measures the time a page takes to load its main contents while rendering the largest elements.
When above-the-fold contents become visible on the viewport, the largest elements take more time than other main elements.
Thus, to measure page load speed, it’s highly effective to calculate the time it takes to download the largest elements on a web browser.
Contents like images, videos, SVG, and background images loaded through the ‘url()’ function are considered as the largest contents.
Standard LCP Score
To Google’s standard, if your site loads in less than 2.5 seconds, that’s great. You might need to make improvements if it’s between 2.5 to 4.0 seconds.
But, taking more time than that? You really need to work on it and improve its loading performance if it’s more than 4.0 seconds.
What causes a poor LCP score?
- Slow Server Response Time
- Blocking JavaScript and CSS while rendering
- Client-side rendering
- Large Elements takes longer load time
Ways to Solve those issues
You have several ways to solve the loading time issue to improve LCP score. But you have to first identify what causes your website loading slow?
If you are facing a slow server response time, you can try using a nearby Content Delivery Network (CDN). Also can try to do Server-Side Caching or can establish early third-party connections.
When render blocking time is causing the problem, try to compress CSS & JavaScript files, remove unnecessary scripts, and try to optimize your codes.
You can also optimize large files like images, compress text files, preload essential resources and server side rendering.
First Input Delay (FID)
This metric measures interactivity of web pages. An interactive website or webpage involves users more and increases site engagement.
FID measures the response time when a user interacts with a section like a call to action button, link, or a custom JS feature.
For example, a user taps on a button that is supposed to show a popup on-click. The metric will measure the time the web page takes to show the popup on-screen after the button is clicked.
So, FID is the delay time between a call made and the action to perform for an interactive section. This delay time or response time is actually the FID score that search engines measure.
Standard FID score
Google considers pages with First Input Delay (FID) of under 100 milliseconds as good. Anything between 100 to 300 mS is considerable. However above 300 milliseconds is labeled as poor.
What causes the delay?
- Large JavaScript bundles
- Loaded main thread
- Long running JavaScripts
Ways to solve those issues
To reduce the first input delay time, you can try splitting long tasks into smaller ones. Break down large codes and reduce the amount of JavaScript loading on an individual page.
Reduce main thread blocking time by using a web worker. A web worker will move non-UI operations to a different worker thread.
Also, reduce JavaScript execution time by holding off the unused JavaScript and minimizing unused polyfills.
Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)
The Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) benchmark is set to ensure a smooth and natural shift of contents. It measures visual stability.
What is actually visual stability? Let’s describe this with an example.
Suppose, someone is reading an article on your site, and all of a sudden a popup shows up. Or, contents start moving, without any warning.
We all know how irritating that is from the user’s point of view. Lack of stability causes enough harm to web performance.
To deliver better visual stability, a smooth and natural shift of contents is essential.
CLS metric quantifies surprising shifts of contents on a page and helps to make sure that the page performance is as satisfying as possible.
Standard FID score
CLS core below 0.1 is good for the site’s stability. A score less than 0.25 is still adequate. But Google considers sites that have higher CLS score than 0.25 as poor for visual stability.
What causes the poor CLS?
- Images and Videos without Dimensions
- Ads, Embeds, iframes without Dimensions
- Dynamically injected contents
- Web Fonts causing a flash of unstyled text
What causes the poor CLS?
A great best practice is to define the width and height attribute of images and videos. The web browser allocates specific space for it during page loads.
In terms of responsive web design, you can use CSS aspect ratio. There are some different ways to assign aspect ratios.
Try to allot the size of ads, iframes, and embeds. You can reduce ad slot size, for minimizing layout shifts caused by these elements.
Always avoid dynamically injected contents. The best practice is to avoid inserting unexpected dynamic contents. Only show those contents when a user interacts to see those contents.
Standard Core Web Vitals Score
| Good | Needs Improvement | Poor | |
|---|---|---|---|
|
LCP
|
<= 2.5s
|
<=4.0s
|
>4.0s
|
|
FID
|
<= 100 ms
|
<=300ms
|
>300ms
|
|
CLS
|
<=0.1
|
<=0.25
|
>0.25
|
Note: All Data source is “web.dev” which article published on Apr 30, 2020.
How big this change is going to be?
There are scads of ranking signals that set websites rank on search results. Still, experts are considering Web Vitals as a serious ranking factor.
Many of the experts have suggested that Google aims to prioritize user experience above other factors. This actually a positive change, both from user’s perspective and site owner’s.
As a developer or a site owner, you don’t have to do much. Just keep your site clean, work on its interactivity, and make the transitions smooth and natural. Also, make sure site is loading fast enough.
Just those regular things would make your website more useable.
It’s easy to check your sites Core Web Vitals status on Google Search Console in the enhancement section.
If your site hasn’t passed those parameters, start optimizing your site for web vitals right now. You surely don’t want to fall behind in the ranking race.
Recently Google Search Central has been published a blog for their upcoming update. They discussed-
– Gradual rollout starting in mid-June this year.
– Details on what will be included in the update.
– A new Page Experience report in Search Console.
– Support for signed exchanges for all content on Google Search.
Exclusive Addons stands out on Core Web Vitals metrics
People often concern about web performance of WordPress sites.
In truth, some of the third party plugins or addons do actually cause some problems.
With Exclusive Addons though, you can keep that concern away! Our widgets, extensions, and elements set a very good score on each Core Web Vitals signal.
While developing the plugin, we have optimized the codes and left out everything that is unnecessary or may slow down your website. That makes our widgets lightweight and super fast.
Exclusive elements could easily maintain LCP to less than 2.5 sec. Although loading seeping depends on lots of factors, including server speed and all.
Response rate is of our widgets are high enough to set FID a good score. When a user clicks on an interactive section, elements will at least respond within 100 milliseconds.
Visual stability will actually depend on your design. Our incredibly customizable options will let you set a smooth transition of contents on web pages. And we’ve ensured that none of our element causes visual instability.
Wrapping it up….
SEO signals are the best way to tell search engine that why should rank you above others. These signals fairly draw a holistic picture about user experience quality on your web page.
Web vitals, the upcoming ranking change factor is going to be in action any time soon in 2021. And with that, there is a lot to change in the SEO world.
Incorporating page experience matrics, Google has made it clear that what they are aiming for.
Now is the best time for you to take a fresh look at your web performance, understand Core Web Vitals. And most importantly, make your website more user friendly.
If you’re using Elemenetor page builder, you may already know Exclusive Addons going to help you with that.
Faster loading speed, better interactivity, and perfect visual stability everything that Core Web Vitals requires.
To change your page building experience with Elementor, our first and foremost concern has always been providing the best experience to the users.
